Ascites Is Best Defined as Which of the Following
Normally the peritoneal cavity contains 2550 mL of ascitic fluid which allows for the movement of bowel loops past one other and helps hydrate serosal surfaces. None of the.
Abnormal accumulation of serous fluid in the spaces between tissues and organs in the cavity of the abdomen called also hydroperitoneum.

. Handbook of Clinical Neurology 2017. Ascites is defined as accumulation of more than 25 ml of fluid in the peritoneal cavity. Ascites refers to the buildup of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Raises capillary hydrostatic bed within the sphlancnic circulation. Symptoms may include increased abdominal size increased weight abdominal discomfort and shortness of breath signs may be absent if fluid accumulation is 1500 ml It can result from hepatic disorders usually chronic but sometimes acute. Ascites ay-SITE-eez is when too much fluid builds up in your abdomen belly.
Fluid may also move into your chest and surround your lungs. Alcohol abuse over many years. 14 mg dL D.
Patients with cirrhosis who develop ascites have a 50 2-year survival. Ascites related to portal hypertension cirrhosis congestive heart failure Budd-Chiari is generally higher than 11. If severe ascites may be painful.
HRS is seen in patients with refractory ascites D. 13 mg dL C. 12 mg dL B.
Ascites denotes pathologic accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity 25 mL and is the most common complication of cirrhosis. Diseases that can cause severe liver damage can lead to ascites. The problem may keep you from moving around comfortably.
Ascites can set the stage for an infection in your abdomen. -A small amount of fluid is normally found within the abdominal cavity. Ascites results from high pressure in the blood vessels of the liver portal hypertension and low levels of a protein called albumin.
Accumulation of at least 2L of fluid in the abdominal cavity. How much fluid is normally found within the abdominal cavity. Causes Ascites results from high pressure in the blood vessels of the liver portal hypertension and low levels of a protein called albumin.
Ascites is defined as an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. In the developed world. Some of the common risk factors that cause the ascites are as follows.
What are the two main causes of ascites. Ascites is the abnormal build-up of fluid in the abdomen. Ascites is defined as accumulation of free fluid in the peritoneal cavity.
It is the most common complication of cirrhosis with approximately 50 of persons with compensated cirrhosis developing ascites over the course of 10 years. Medical Definition of ascites. Based on the severity of fluid accumulation ascites can be categorized as mild moderate and large.
Renal failure in cirrhosis is defined as serum creatinine above. The amount has not been defined formally however it is noted that physiologically there is 50-75 mL fluid in the abdominal cavity. Which of the following about hepatorenal syndrome is false.
Uncomplicated and refractory ascites. So when only a small amount of fluid is present which might be physiological radiologists tend to use the. -Ascites is the accumulation of fluid within the abdominal cavity and is a common cause of abdominal distention.
If abdominal distention or bloating of the belly is present. This is called the Serum Ascites Albumin Gradient or SAAG. Portal hypertension is required for development of cirrhotic ascites as individuals with HVPG less than 12 mm Hg do not develop this complication.
In Western countries development of ascites is in 75 of cases due to underlying cirrhosis European Association for the Study of the Lever 2010 but other less common etiologies of ascites such as malignancy congestive heart failure Budd Chiari syndrome tuberculosis and. Ascites is a condition in which fluid collects in spaces within your abdomen. Type I HRS carries a mortality rate of 90 C.
Ascites plural is same word tends to be reserved for relatively sizable amounts of peritoneal fluid. A transudate is due to increased pressure in porta vein 8mmhg generally around20mmhg Exudates are generally secreted in response to inflammation or malignancy. After developing ascites that necessitates hospitalization the risk of mortality.
Upon physical examination a doctor may determine that a person has ascites if there is presence of the following. Type I HRS is the more aggressive form B. There are two different types of ascites.
This makes it hard to breathe. A sheet of tissue called the peritoneum covers the abdominal organs including the stomach bowels liver and kidneys. Ascites caused by other reasons malignant pancreatitis is lesser than 11.
This condition often happens in people who have cirrhosis scarring of the liver. Portal hypertension varicosities splenomegaly esophageal varices with caput medusa splenomegaly gastrointestinal hemorrhage hematemesis ascites edema altered sex hormone metabolism hepatic encephalopathy and jaundice. Complications can include spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.
Importantly sinusoidal hypertension appears to be a requirement for development of ascites. Portal hypertension and primary peritoneal diseases. Ascites is free fluid in the peritoneal cavity.
Conditions unrelated to the liver can. Ascites is defined as the pathological accumulation of excess fluid in the peritoneal cavity. The sides of the abdomen or flanks are pushed outward.
Ascites The pathological accumulation of serous fluid in the peritoneal abdominal cavity which common in the decompensated advanced liver disease and develops in 50 of those with cirrhosis. Technically it is more than 25 ml of fluid. Technically it is more than 25 ml of fluid in the peritoneal cavity although volumes greater than one liter may occur.
How does Portal Hypertension paly a role in the formation of ascites. Loss of appetite nausea indigestion weakness blood backing and weight loss. Chronic hepatitis C or B infection.
Ascites Mild and nonspecific. Symptoms may include increased abdominal size increased weight abdominal discomfort and shortness of breath. Ascites is the build-up of fluid in the space between the lining of the abdomen and abdominal organs.
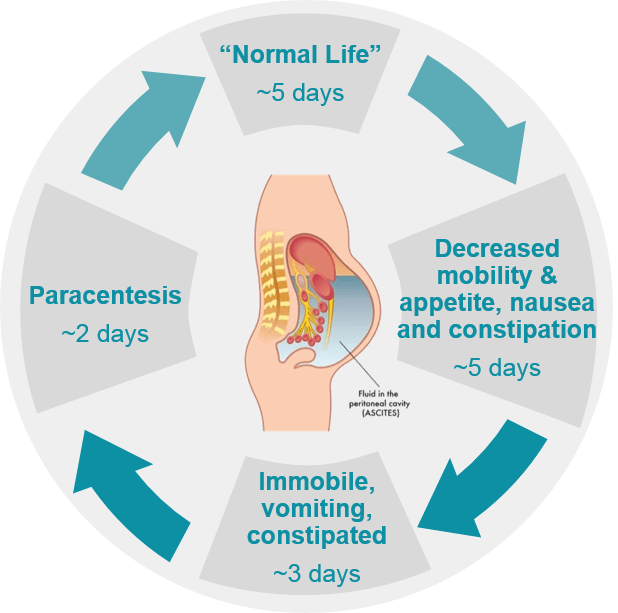
Liver Disease Nash And Ascites Sequana Medical

Ascites Nursing Diagnosis And Nursing Care Plan Nursestudy Net

Ascites What Is It Causes Appearance Treatment And More Osmosis

Congestive Heart Failure Congestive Heart Failure Heart Failure Cardiac Nursing
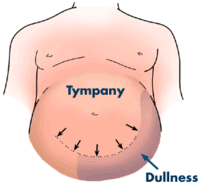
Techniques Liver Ascites Exam Physical Diagnosis Skills University Of Washington School Of Medicine

Ascites Ayurvedic Treatment Sunburn Relief Instant Medical Knowledge

Pin By Andrea Donzelli Nail Design On Rn Nursing School Survival Perioperative Nursing Nursing Study Tips

New Paracentesis Cpt Code 2013 Medical Coding Guide How To Code Medical Coder Medical Coding Medical Billing And Coding

Treating Fluid In The Abdomen Fluid In The Abdomen Cancer Research Uk

What Causes Ascites Symptoms Treatment Diagnosis Prognosis
Ascites Macmillan Cancer Support

Ascites Symptoms Causes Treatment Nursing Times
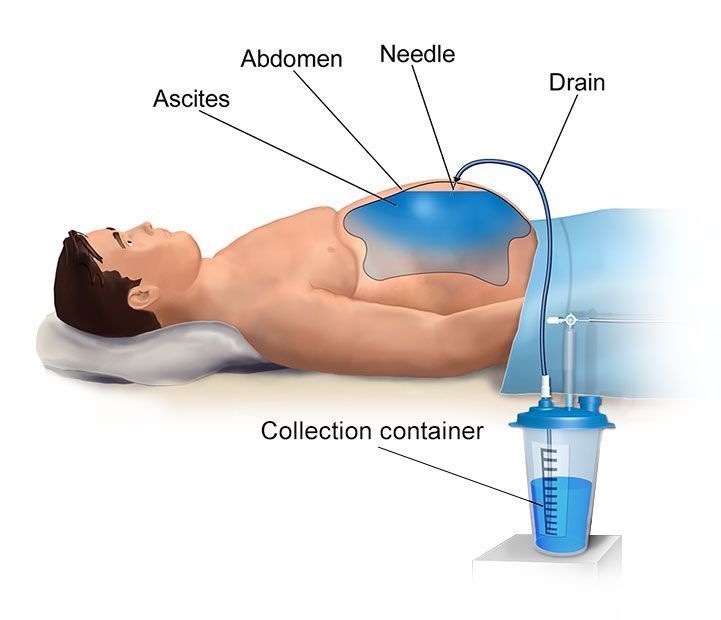
Liver Disease Nash And Ascites Sequana Medical

Leveen Shunt Transfers Ascites Fluid To The Superior Vena Cava I Don T Think This Is Done Anymore Medical Dictionary Medical Terms Medical

Pin On Gastrointestinal Disorders

Hepatic Encephalopathy Nursing Management Rnpedia Brain Diseases Disease Medical Mnemonics



Comments
Post a Comment